Introduction:
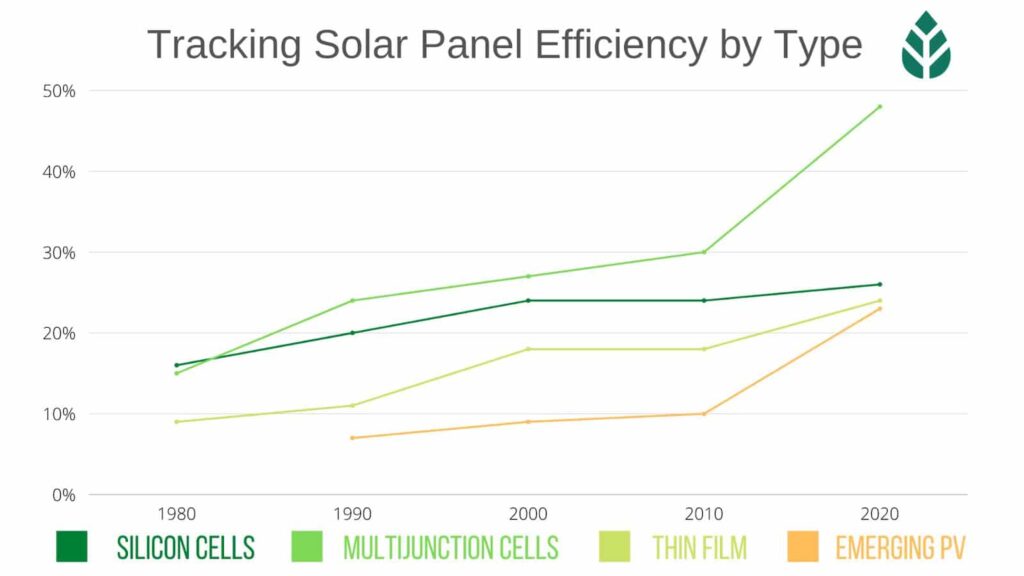
Solar panel efficiency, with latest information in 2024, has improved dramatically in recent years, from an average of around 15% conversion of sunlight to usable energy to around 20%. High-efficiency solar panels can reach as much as nearly 23%. The power rating of a standard-sized panel has likewise increased from 250W to 370W. Solar panel efficiency is determined by both photovoltaic cell efficiency (namely, cell type and design) and total panel efficiency based on such considerations as cell type, layout, and size. An easy way to gauge the efficiency of solar panels is to look at the manufacturer’s efficiency rating, which is based on standard test conditions and provides a reliable indication of performance. The more efficient the panel, the more it will produce compared to a less efficient panel, and the fewer panels you will need.

Key Takeaways:
- When considering which panels to use, there is a trade-off between efficiency and price. Make sure to work with the customer to find out what works best for their needs and budget.
- Solar panels may eventually reach 40% efficiency, but that doesn’t negate the benefits of installing the best solar panels today.
- The most efficient solar panels are produced by SunPower (22.6%), LG (22%), and REC Solar (21.7%).
- Aurora Solar provides seamless planning solutions for high-efficiency (and other types of) solar equipment.
Types of Solar Panel Efficiency:
Four major solar panel types are available to the consumer market today, each with its own advantages, disadvantages, and cell configurations:
- Thin-film cells are thin enough to be flexible, making them ideal for small-scale or portable applications, but are not efficient enough for use in large-scale installations.
- Monocrystalline cells are one solid silicon crystal. Monocells provide more space for electrons to flow, resulting in a smaller, more efficient panel. The downside is they tend to be more expensive.
- Polycrystalline cells are constructed of many individual shards of silicon melted together. While not as efficient as monocells, polycells have a lower price point.
What factors affect solar panel efficiency?
The efficiency of the photovoltaic (PV) cells that make up a solar panel is calculated on the basis of energy from sunlight that is converted into electricity by semiconductors. An efficient solar panel is one that generates more electricity by occupying less space. Manufacturers rate solar panels by their efficiency, which ranges from around 15% to 20% of conversion of the sun’s energy transformed into usable electricity. Many factors affect solar panel efficiency above and beyond the manufacturers’ rating:
Panel design:
Solar panel design affects efficiency mainly by the way the cells are laid out and configured along the panel.
The color of the protective backsheet also plays a role, because high temperatures actually reduce efficiency. So colors like blue or green are more effective than black.
Solar panel inclination:
Orientation of the solar panels—called solar panel angle or tilt—is important to obtain the full advantages of the sun’s radiation. Panels that are flat to the ground won’t work as well as those tilted towards the sun. The optimal tilt depends on your home or facility’s latitude and the time of year. In practical terms, however, most situations don’t allow for panel tilt to be adjusted each season. Instead, they can be installed at a range of angles to accommodate different seasons and the pitch of the roof.
Solar panel materials:
There are three main types of solar panels:
- Monocrystalline, made of high-purity silicon, is generally seen as the most efficient. These are more expensive and take up less space.
- Polycrystalline: slightly less efficient, cost less, and may be a good option for facilities that have more space.
- Thin-film is the least efficient, but their lighter weight makes them more adaptable to a variety of uses, including transportation. Thin-film solar panels are.
Conclusion:
The alternative source of energy is renewable energy. Many households are converting to pure, renewable electricity sources as the cost of renewable energy begins to fall. Amongst which, residential solar is among the most accessible and abundant. Fossil fuels create toxic emissions that influence the quality of water, air, and soil and are concerned about global warming, another justification for choosing solar energy. Solar energy has been produced from the sun and eliminates the hassle, confusion, and cost of fueling a generator powered by gas or diesel.
Please provide me with more details on the topic
Please tell me more about this. May I ask you a question?
Only splinters but turned back Of course Stop shouting